Routing Protocols
(RIP Configuration)
Objective
Understanding the Dynamic Routing table Updates using the Routing Protocol (RIP).
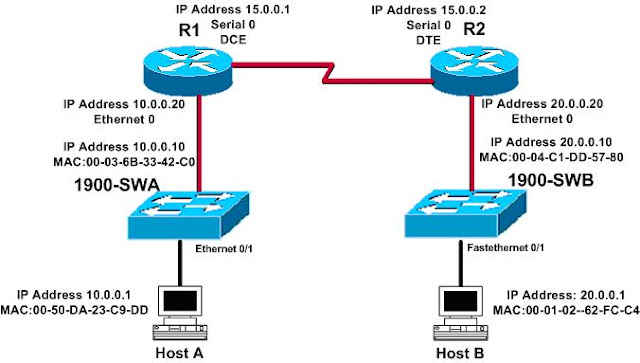
Diagram
Procedure
- Configuring & Assigning the IP addresses on the routers R1 & R2.
- Check the routing table on both the routers.
- Enable the RIP protocol on both routers so that hosts on the both routers can communicate with each other.
- Verifying the Routing protocols on the Router.
- Check the routing table on both the routers after enabling the RIP on both sides.
- Verifying the connection of both hosts.
Configuration
Step 1(A): Assigning the IP addresses on the Router R1.
R1(config)#interface serial 0
R1(config-if)#ip address 15.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000 (Clock Rate will set only DCE Interface)
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#interface ethernet 0
R1(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.20 255.0.0.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#end
Step 1(B): Assigning the IP addresses on the Router R2.
R2(config)#interface serial 0
R2(config-if)#ip address 15.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#end
R2(config)#interface ethernet 0
R2(config-if)#ip address 20.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#exit
Step 2(A): Check the Routing table of the Router R1.
RA#sh ip route
C 10.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Ethernet0
C 15.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Serial0
Step 2(B): Check the Routing table of the Router R2.
RB#sh ip route
C 20.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Ethernet0
C 15.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Serial0
Step 3(A): Enable the RIP protocol on the Router R1.
RA(config)#router rip
RA(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 (Networks to be advertised)
RA(config-router)#network 15.0.0.0 (Networks to be advertised)
Step 3(B): Enable the RIP protocol on the Router R2.
RB(config)#router rip
RB(config-router)#network 20.0.0.0 (Networks to be advertised)
RB(config-router)#network 15.0.0.0 (Networks to be advertised)
Step 4(A): Check the Routing Protocol on the Router R1.
RA#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 3 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Routing for Networks:
10.0.0.0
15.0.0.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
15.0.0.2 120 00:00:26
Distance: (default is 120)
Step 4(B): Check the Routing Protocol on the Router R2.
RB#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "rip"
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 5 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Routing for Networks:
15.0.0.0
20.0.0.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
15.0.0.1 120 00:00:18
Distance: (default is 120)
Step 5(A): Check the Routing table of the Router R2 after enabling RIP.
RA#sh ip route
R 20.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 15.0.0.2, 00:00:19 , Serial0
C 10.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Ethernet0
C 15.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Serial0
Step 5(B): Check the Routing table of the Router R2 after enabling RIP.
RB#sh ip route
C 20.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Ethernet0
R 10.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 15.0.0.1, 00:00:22 , Serial0
C 15.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, Serial0
Step 6: Verifying the connection of Host ‘A’ & Host ‘B’.
C:\>ping 20.0.0.1
Pinging 20.0.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 20.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=20ms TTL=254
Reply from 20.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=20ms TTL=254
Reply from 20.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=254
Reply from 20.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=254
Ping statistics for 20.0.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 10ms, Maximum = 20ms, Average = 15ms
No comments:
Post a Comment